Forest Makers – Learn More
The direct seeding technique is a method to recover native vegetation and bring several economic, social, and ecological benefits.
![]()
ECONOMIC BENEFIT – COMMODITIES VALUATION
Environmental certification is key for rural producers who aim to expand the business to foreign markets. This is because one of the main criteria for certification is the creation of an ecological reserve of native vegetation inside the property premises.
![]()
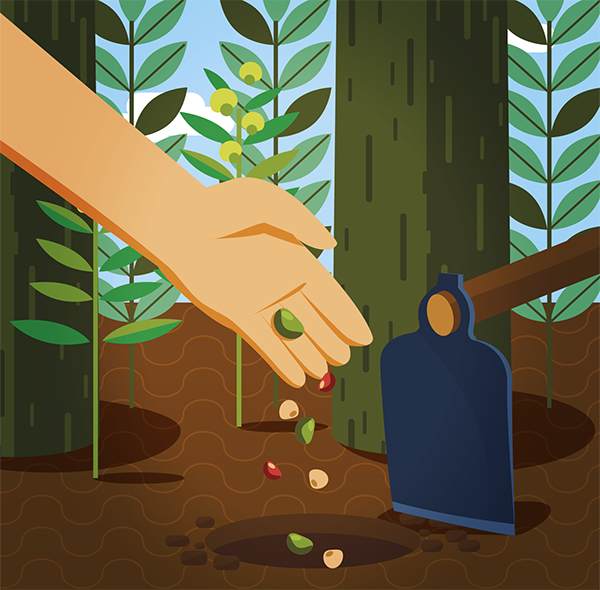
TECHNICAL BENEFIT – SPECIALIZED CONSULTANCY
By contacting the Xingu Seed Network, the rural producer receives advice from engineers specialized in ecological restoration through direct seeding. They will understand the producer’s needs and design a customized project for those needs and the biome. Following the planning, there is also a follow-up throughout all the steps towards restoration.
![]()
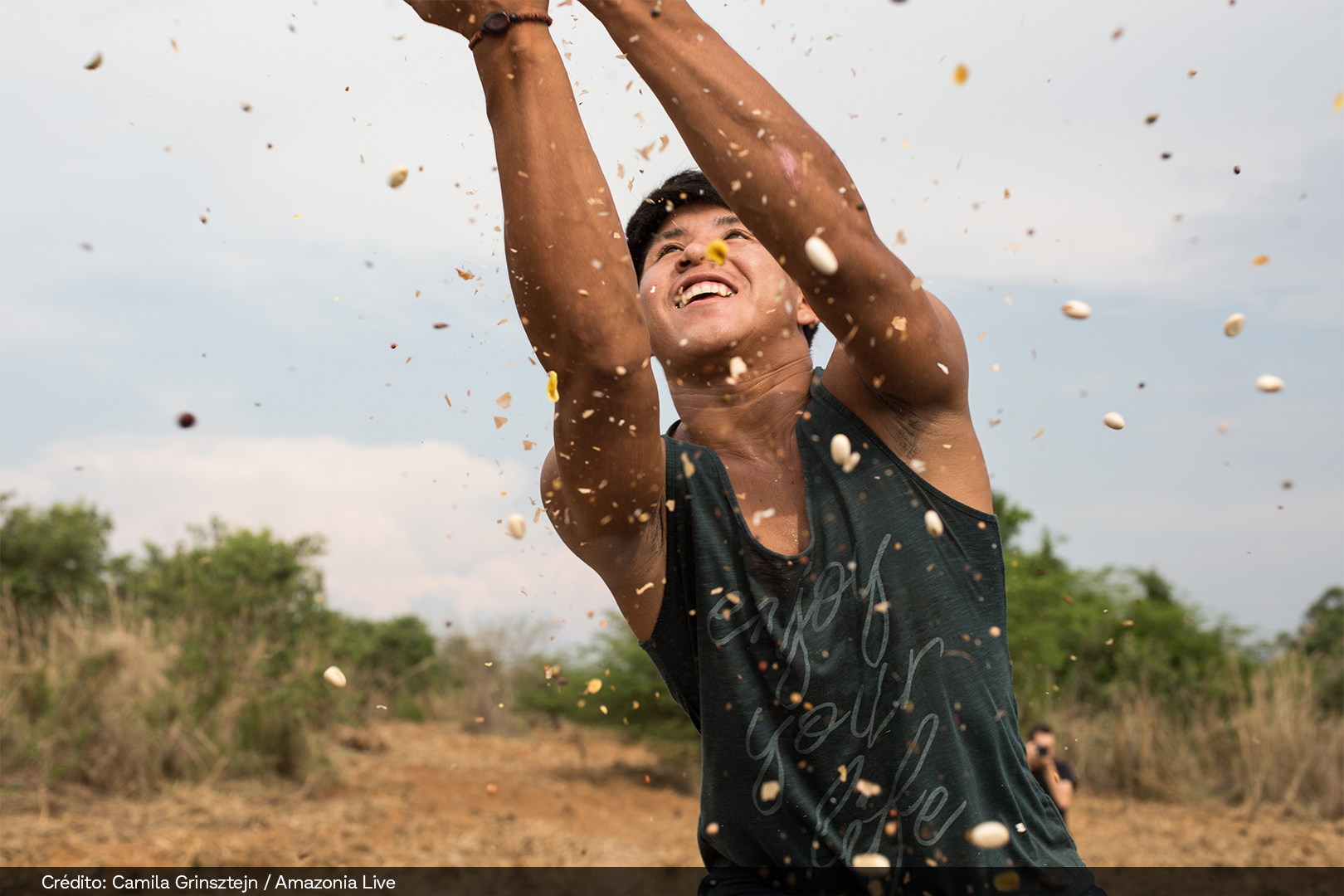
SOCIAL BENEFIT – INCOME GENERATION FOR LOCAL COMMUNITIES
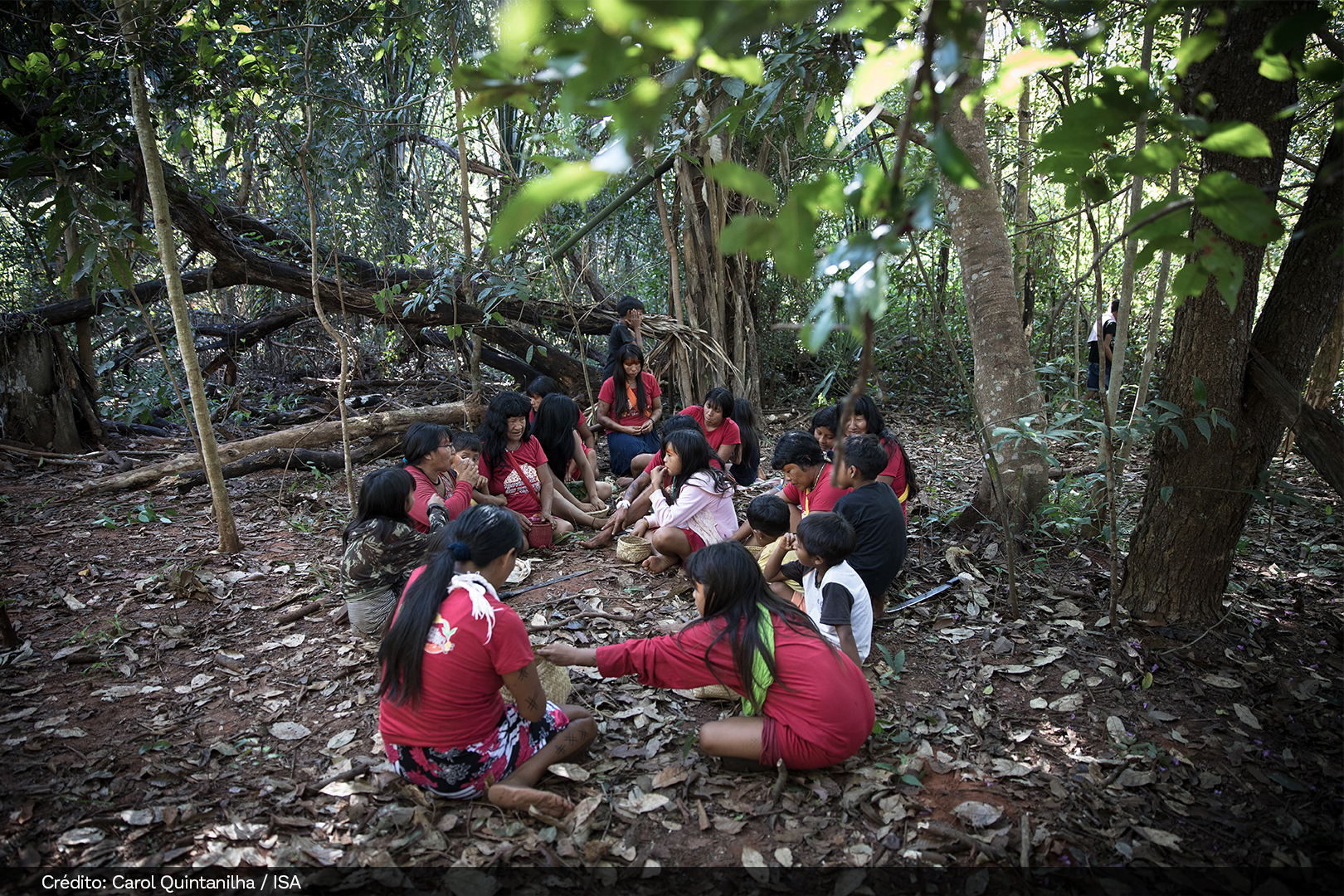
Hundreds of people who work in seed harvesting benefit directly through income generation, knowledge exchange, integration among peer groups, and forest conservation. It is also a way to promote job opportunities for women and traditional communities, such as Indigenous peoples, quilombolas, family farmers, and settlers.
![]()
ECOLOGICAL BENEFIT – RESTORING NATIVE VEGETATION
In a process similar to the natural regeneration of forests in each of the biomes, the direct seeding method favors the growth of trees with well-developed roots, straight trunks, and greater resistance to extreme events (natural disasters).
MORE THAN 6,000 HECTARES HAVE ALREADY BEEN REFORESTED





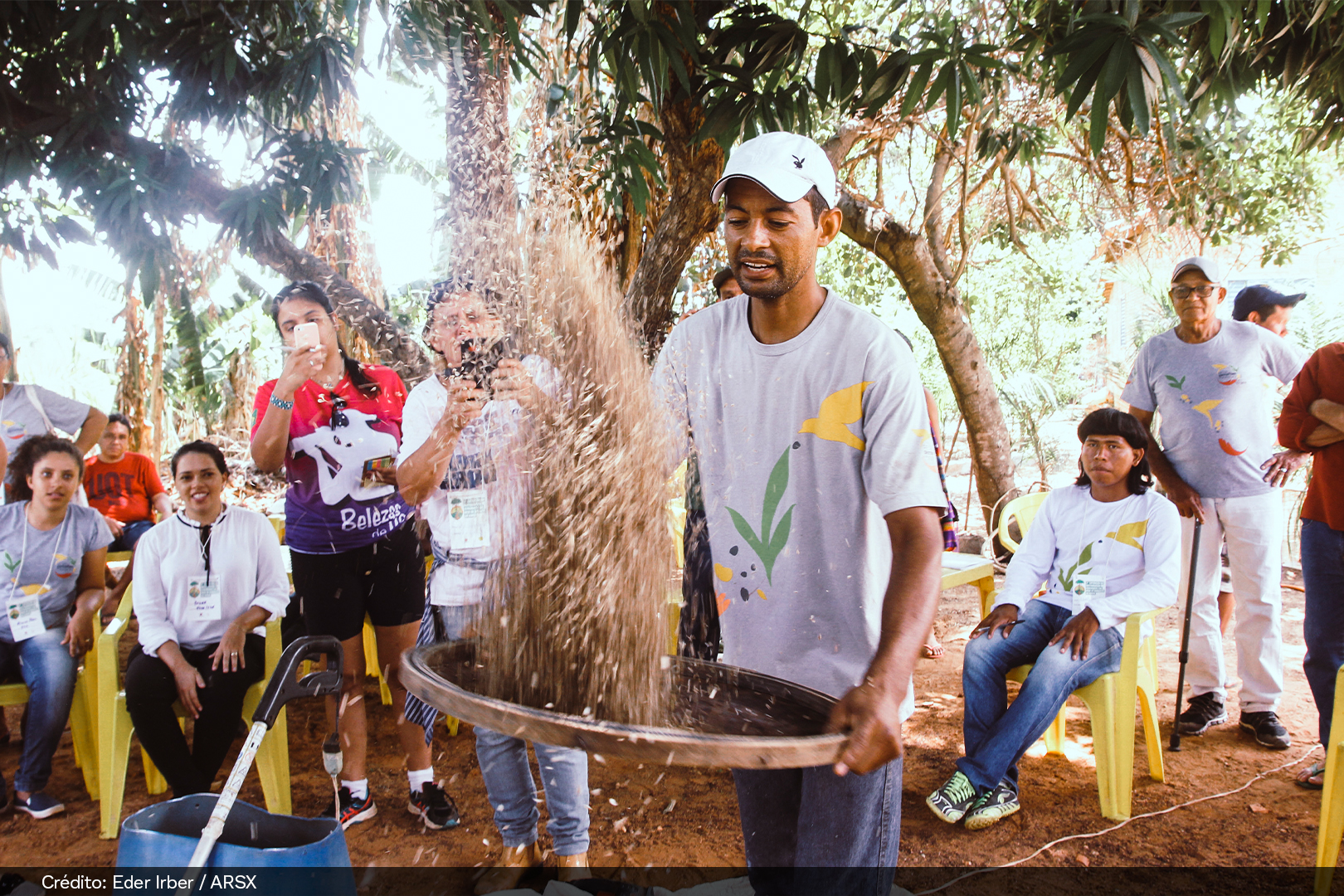
HOW DOES THE SEED MIXTURE (MUVUCA) WORKS
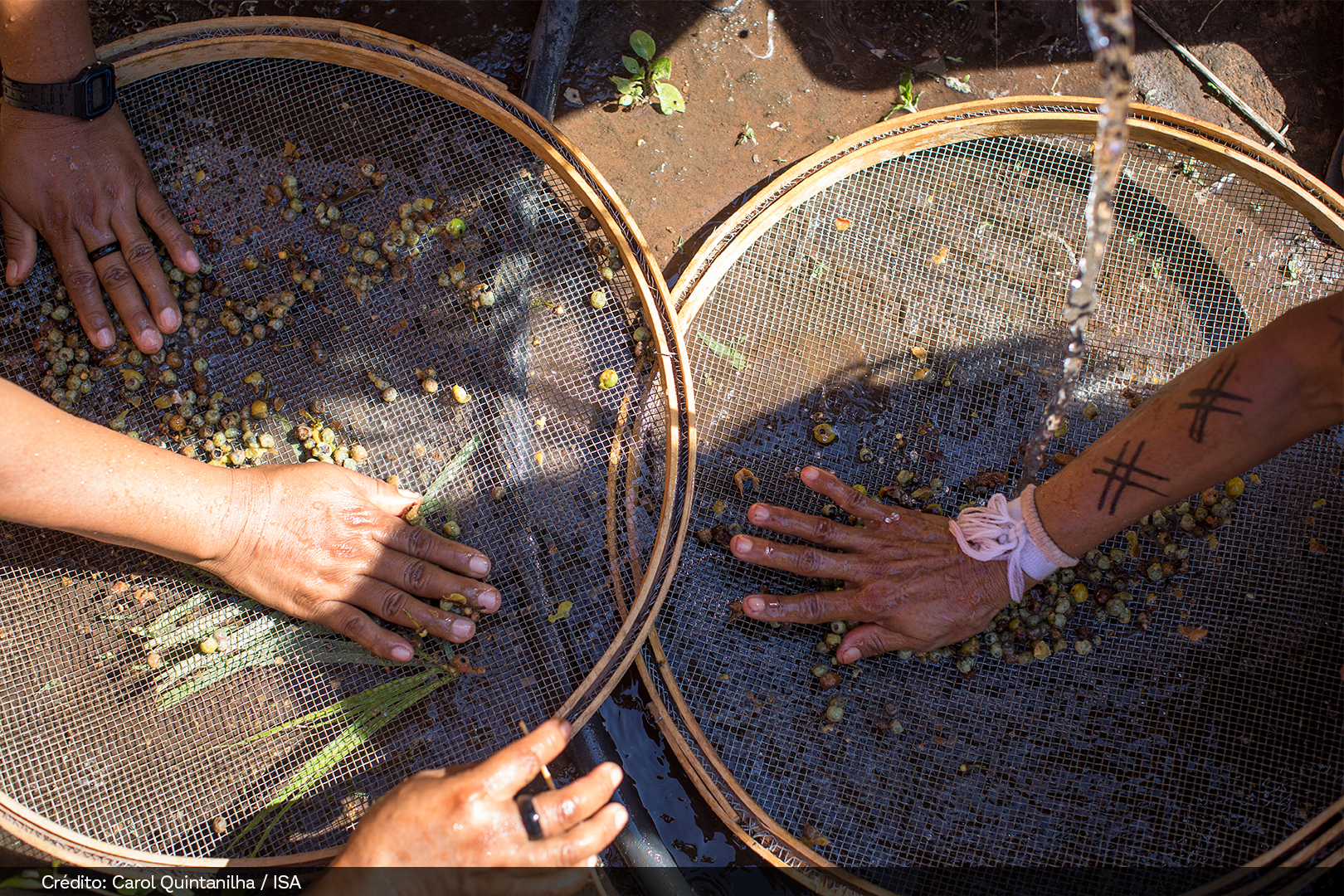
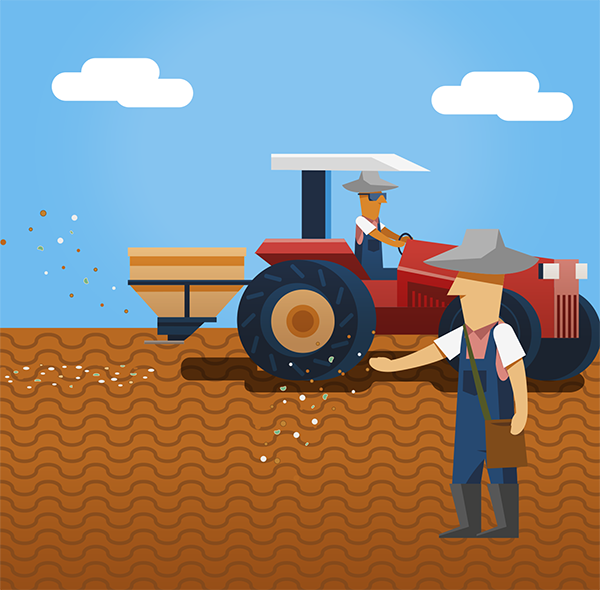
Muvuca is a mixture of seeds of different species to be planted all at once. For centuries, farmers, Indigenous peoples, quilombolas, and traditional communities have been planting native species by direct seeding (a muvuca). There are countless benefits for the quality of the water, fauna, and flora, the climate, agricultural production, and our quality of life.
With the help of the guide below, we want to give you a hand to plant native ecosystems based on the example of a forest in restoration, with trees, shrubs, herbs, and vines.
Your project may need all of these actions or just a few. There is no single recipe. So, come up with your own way of doing direct seeding!
FOREST MAKERS IS PRODUCED BY

The Instituto Socioambiental (ISA) is a Brazilian non-profit civil society organization established in 1994. ISA proposes solutions to social and environmental issues in an integrated manner, focusing on the defense of social, collective, and diffuse goods and rights related to the environment, cultural heritage, and the rights of individuals and peoples.

The Xingu Seed Network Association (ARSX) is a non-governmental, non-profit association considered the most prominent native seed network in Brazil. Created in 2007, the initiative aims to value the peoples and communities that collect seeds for forest restoration in several territories in the watersheds of the Xingu, Araguaia, and Teles Pires rivers. Today, there are more than 500 seed collectors, 20 million trees planted, more than 6 thousand hectares of forests planted, and more than R$ 4.4 million passed on directly to the communities.
WATCH ALSO “FIRE IN THE FOREST”
What has been managed for millennia by Indigenous peoples in opening their crops for subsistence purposes, the fire now rages in an uncontrolled way over the forests due to deforestation in the surroundings of the Xingu area and climate change. For those who dream of getting to know a small portion of the Amazon, “Fire in the Forest” presents the village of the Waurá people, in the Xingu Indigenous Park, Mato Grosso, Brazil, in 360° scenes from the perspective of the threat that hovers over all peoples: the uncontrolled fire.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is muvuca?
What is direct seeding?
The seed mixture includes:
- short-lifecycle legume species used as green manure, such as crotalaria, pigeon pea, and jack bean;
- fast-growing native trees to dominate the canopy;
- slow-growing native trees, dominated by species with orthodox seeds that can be stored.
I want to make a forest on my property. How do I do it?
Can I buy seeds from ARSX for my home/school/place?
I have a planting initiative. Do you donate seeds?
Do you have seeds for agriculture (e.g., corn, beans, rice)?
How can I help the ISA or ARSX?
Follow and promote the work of the Xingu Seed Network on social networks:
Instagram: https://instagram.com/sementesdoxingu
Twitter: https://twitter.com/redexingu
Can I visit the ARSX?
My property is in another biome. Are there other seed banks I could look for?
Learn more about other networks:
- Rede de Sementes do Vale do Ribeira (SP)
- Rede de Sementes do Cerrado (DF)
- Rede de Sementes do Portal da Amazônia (MT)
- Rede de Coletores e Restauradores das Nascentes Geraizeiras (MG)
- Associação Cerrado de Pé (GO)
- Rede de Sementes da Hileia Baiana e Instituto Arboretum (BA)
- Rede de Sementes do Vale do Rio Doce (MG e ES)
- Verde Novo Sementes Nativas (DF)
- Rede de Sementes do Projeto de Integração do São Francisco – Núcleo de Ecologia e Monitoramento Ambiental NEMA/UNIVASF (PE)
- Xingu Seed Network (PA)
- Rede de Sementes Mudas do Rio Doce (MG)
- Sementes do Paraíso (MG)
- Sementes Monjolinho (SP)
Can I screen the film at my school/work/lecture?
TAKE ACTION
More than ever, the protection of the environment and Indigenous peoples needs your support. Support ISA’s various programs and projects.
DOWNLOAD THE CAMPAIGN MATERIALS AND SUPPORT THE INITIATIVE ON YOUR SOCIAL NETWORKS.
#FORESTMAKERS
Share the movie on your social networks
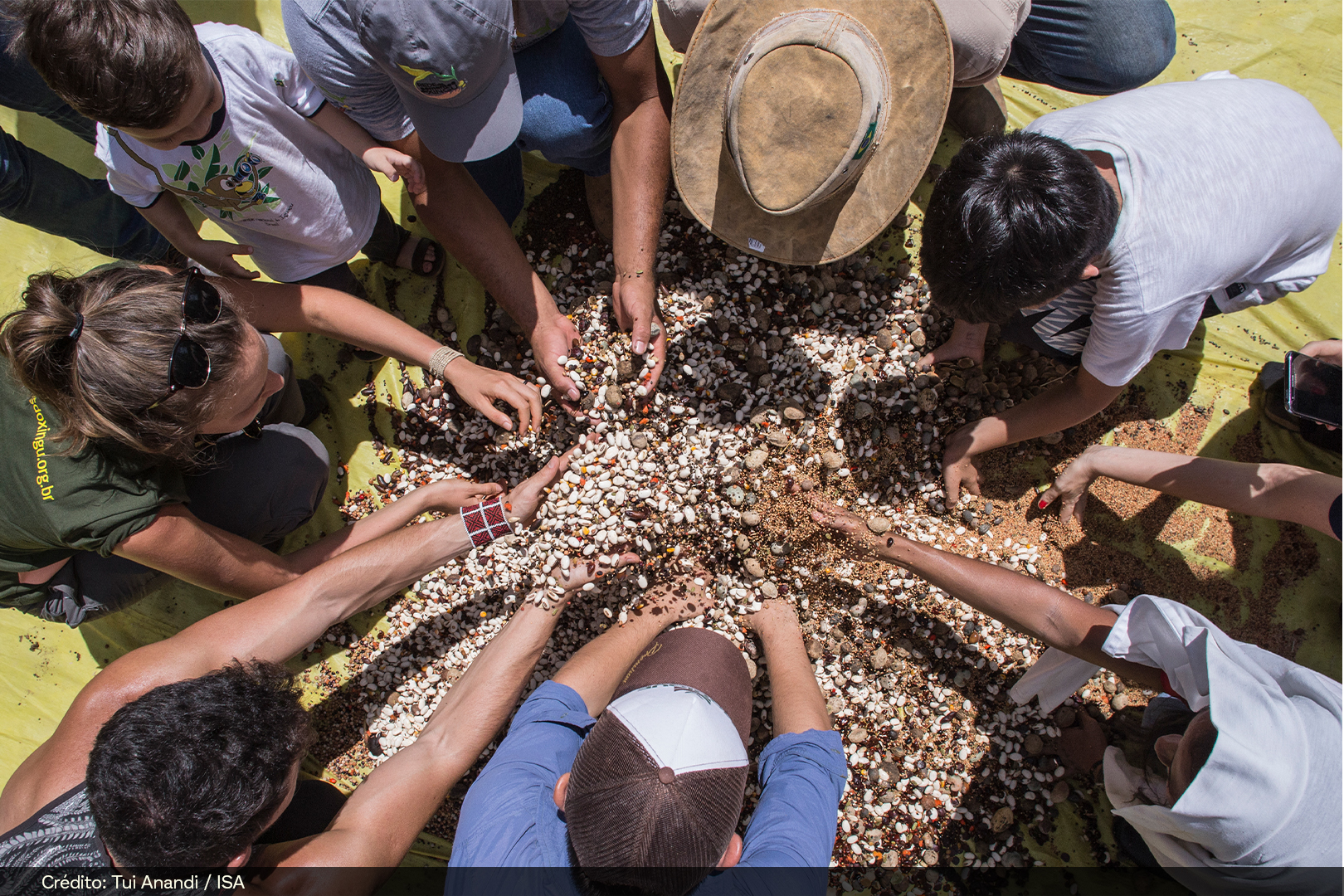
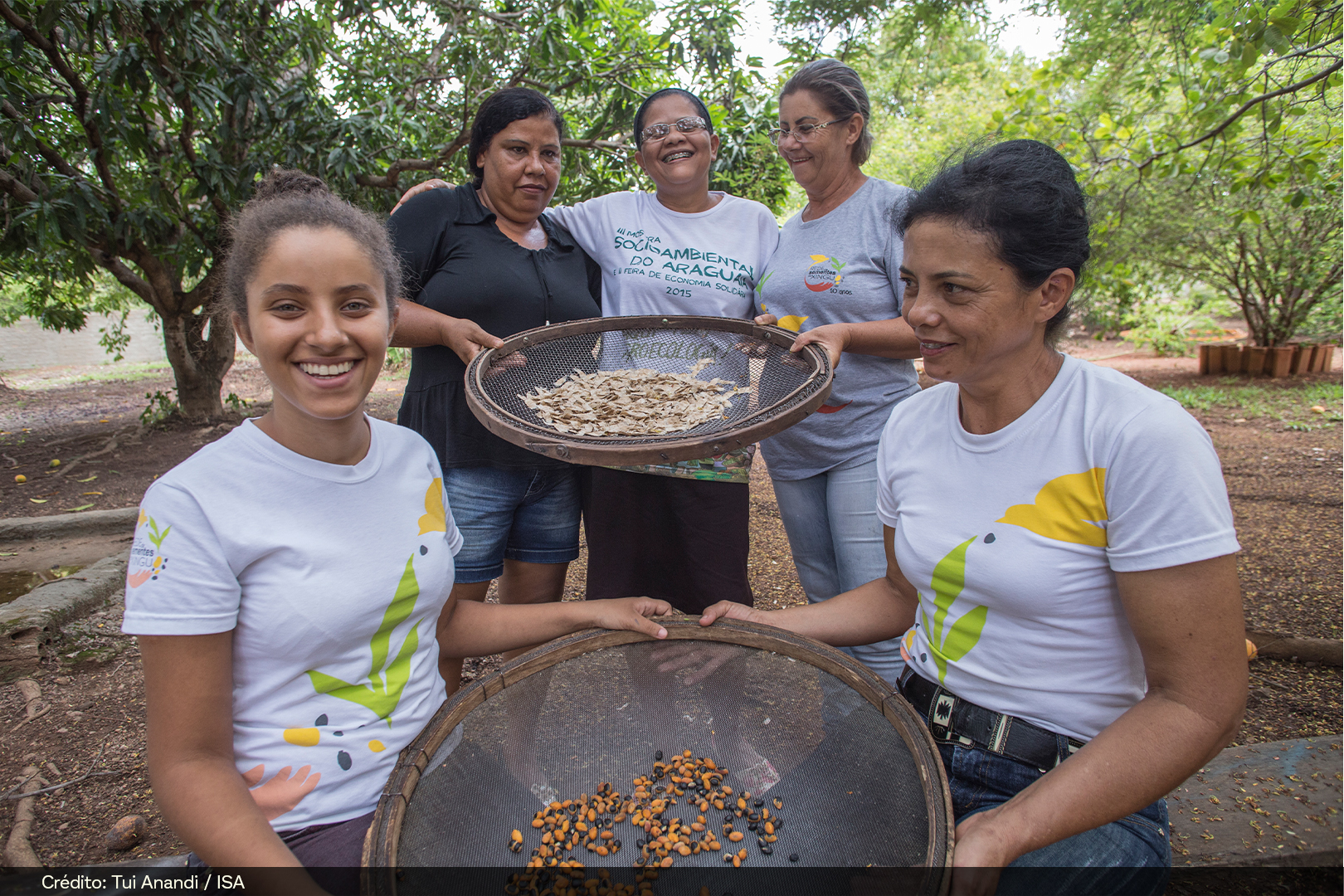
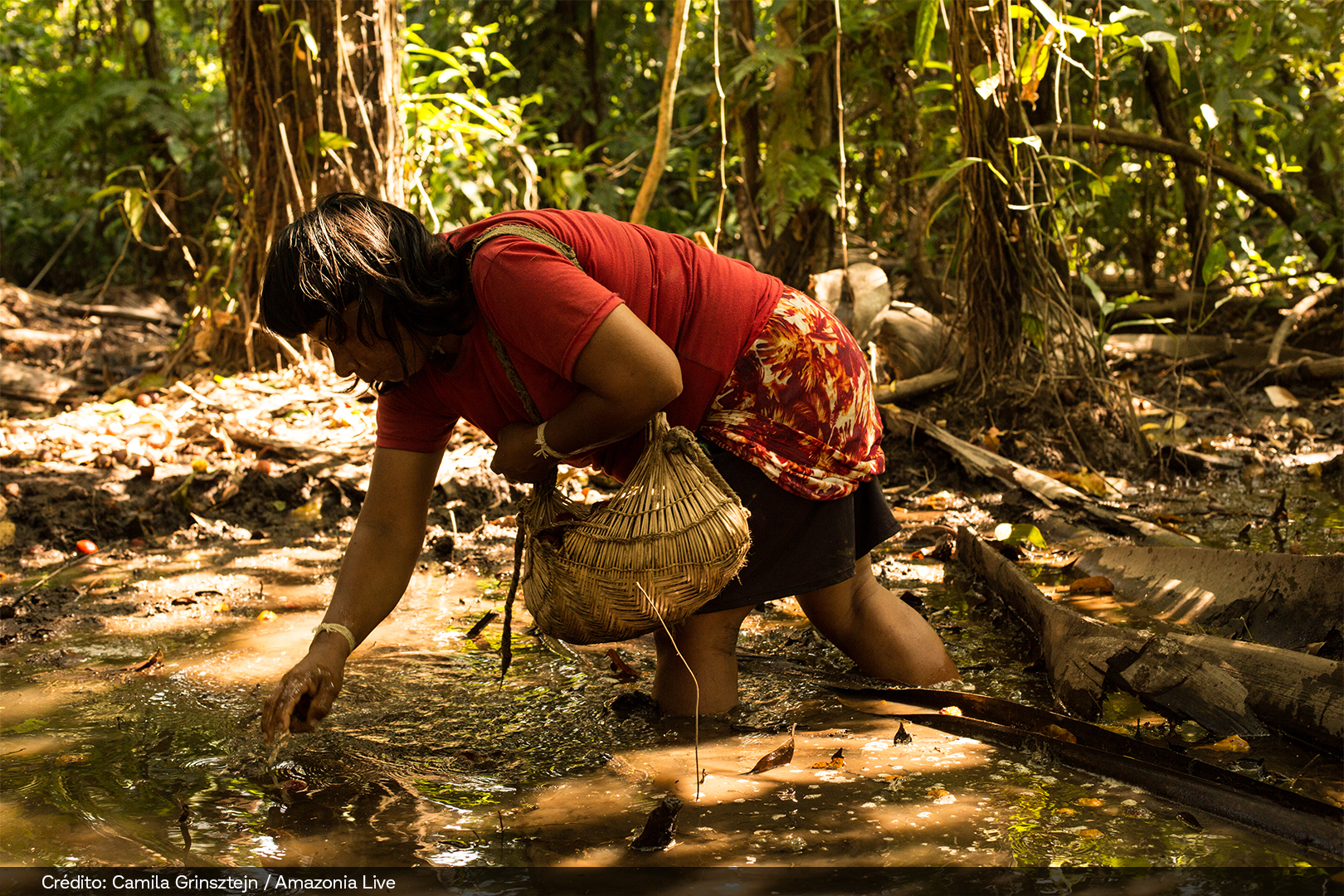
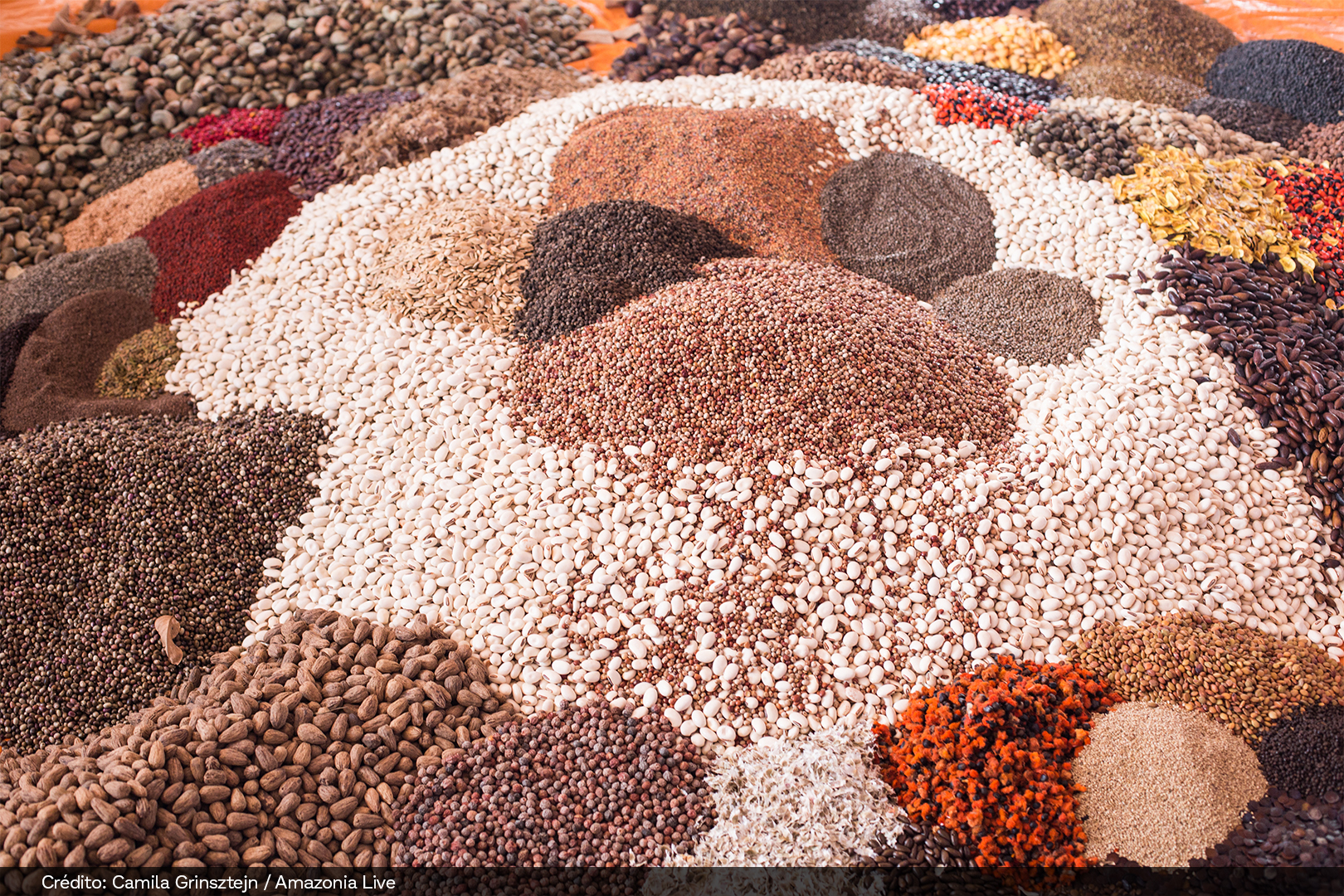
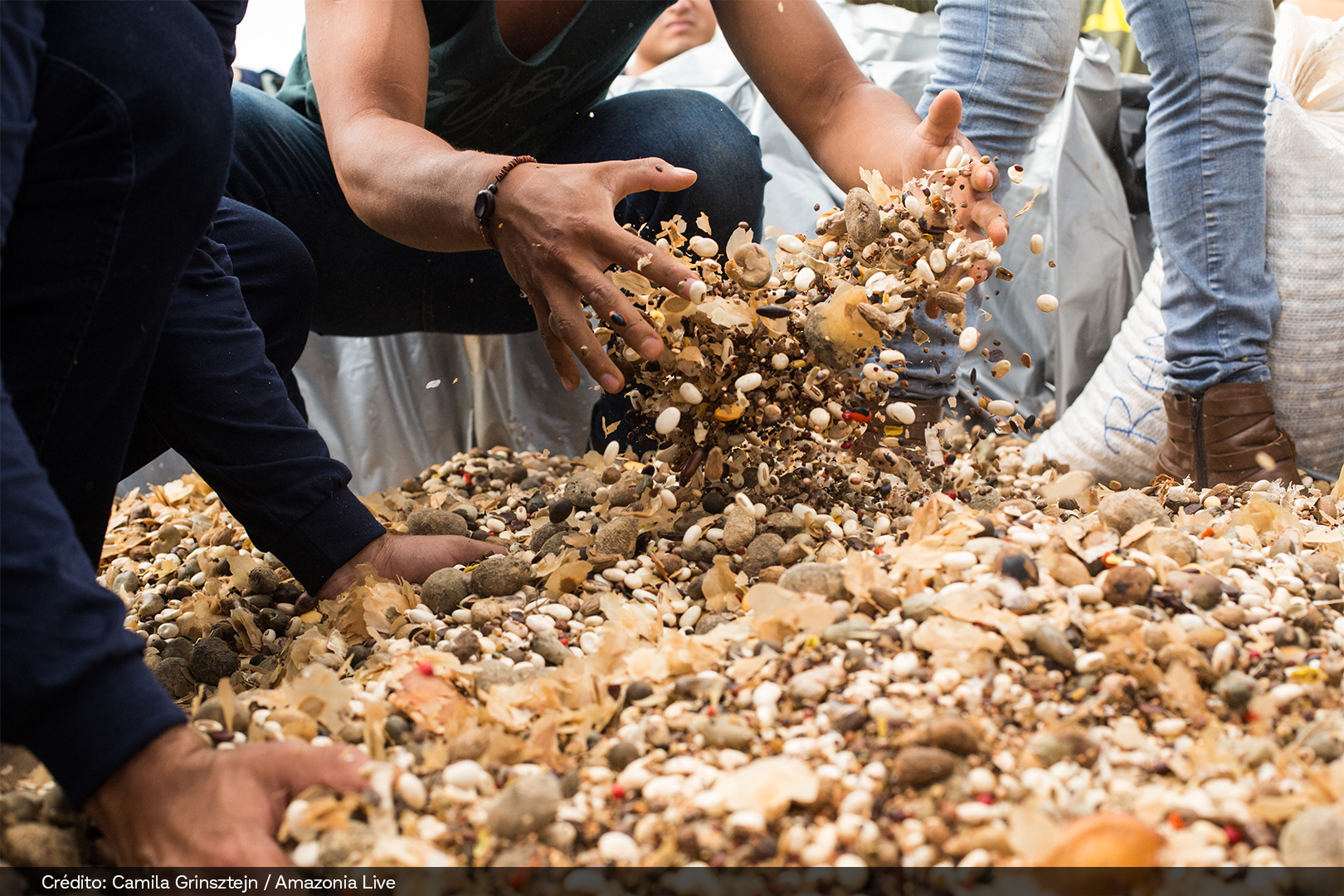
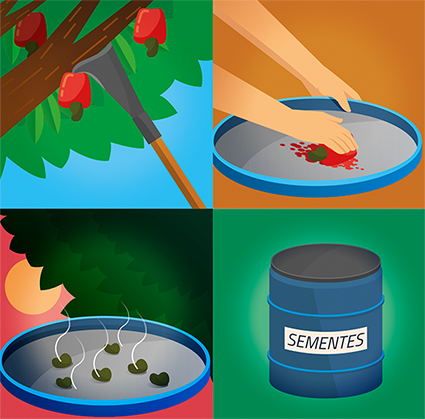
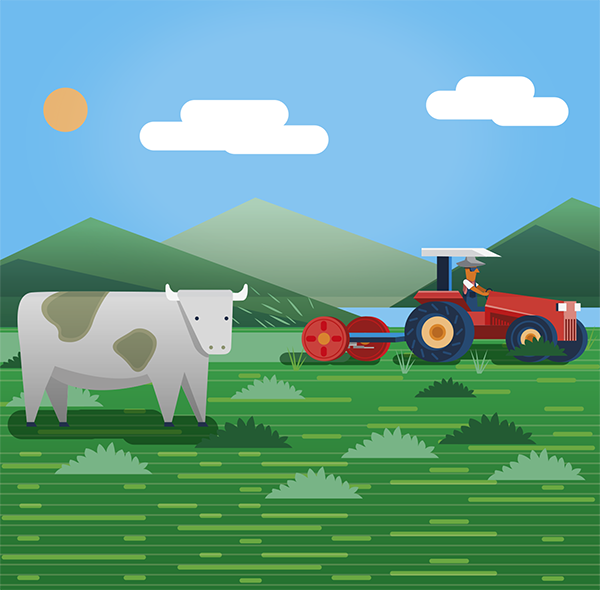
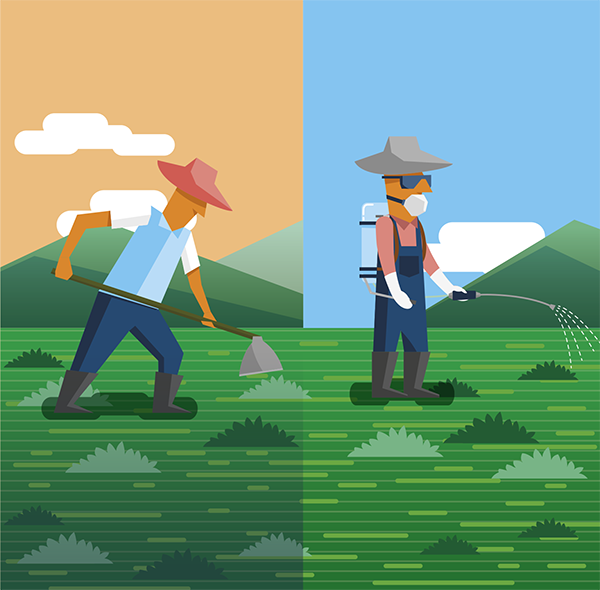
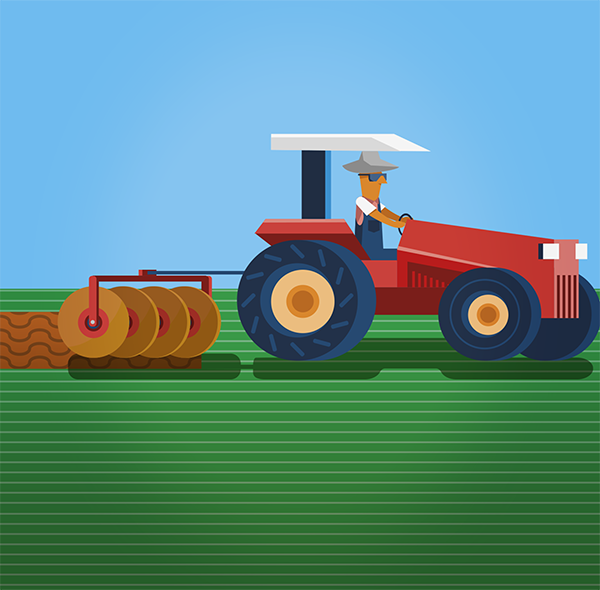
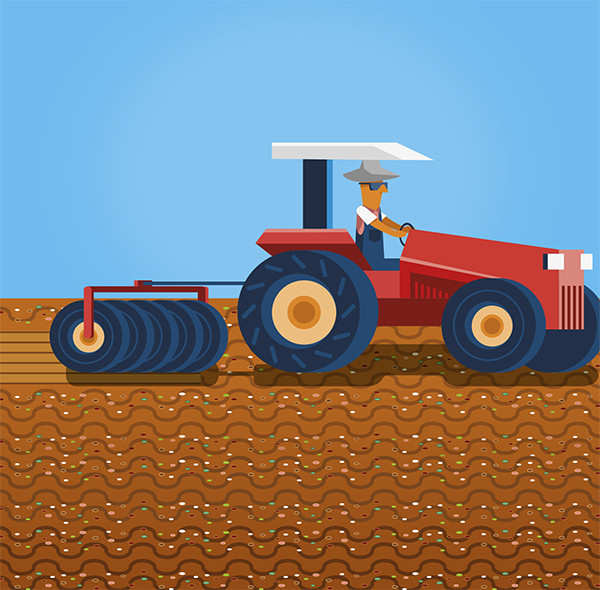




















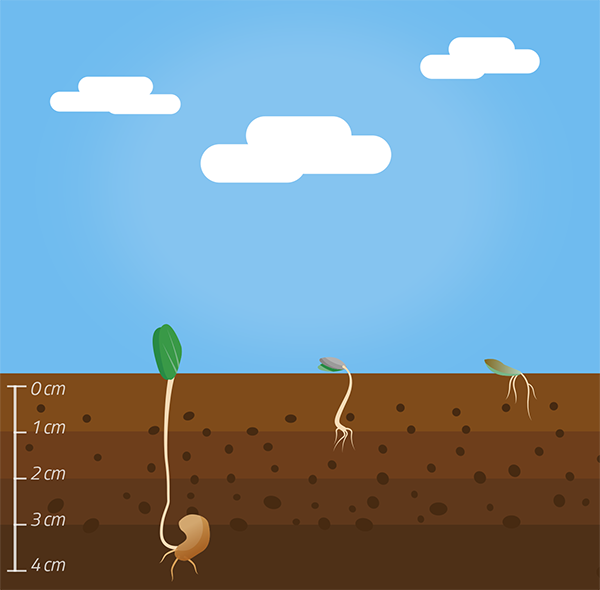






 After scattering the seeds, it is necessary to bury them between 1 and 4 cm deep and carry out another surface soil revolving. This can be done with a tractor, and a leveling harrow closed, a tire roller, or manually, with a rake.
After scattering the seeds, it is necessary to bury them between 1 and 4 cm deep and carry out another surface soil revolving. This can be done with a tractor, and a leveling harrow closed, a tire roller, or manually, with a rake.